Description
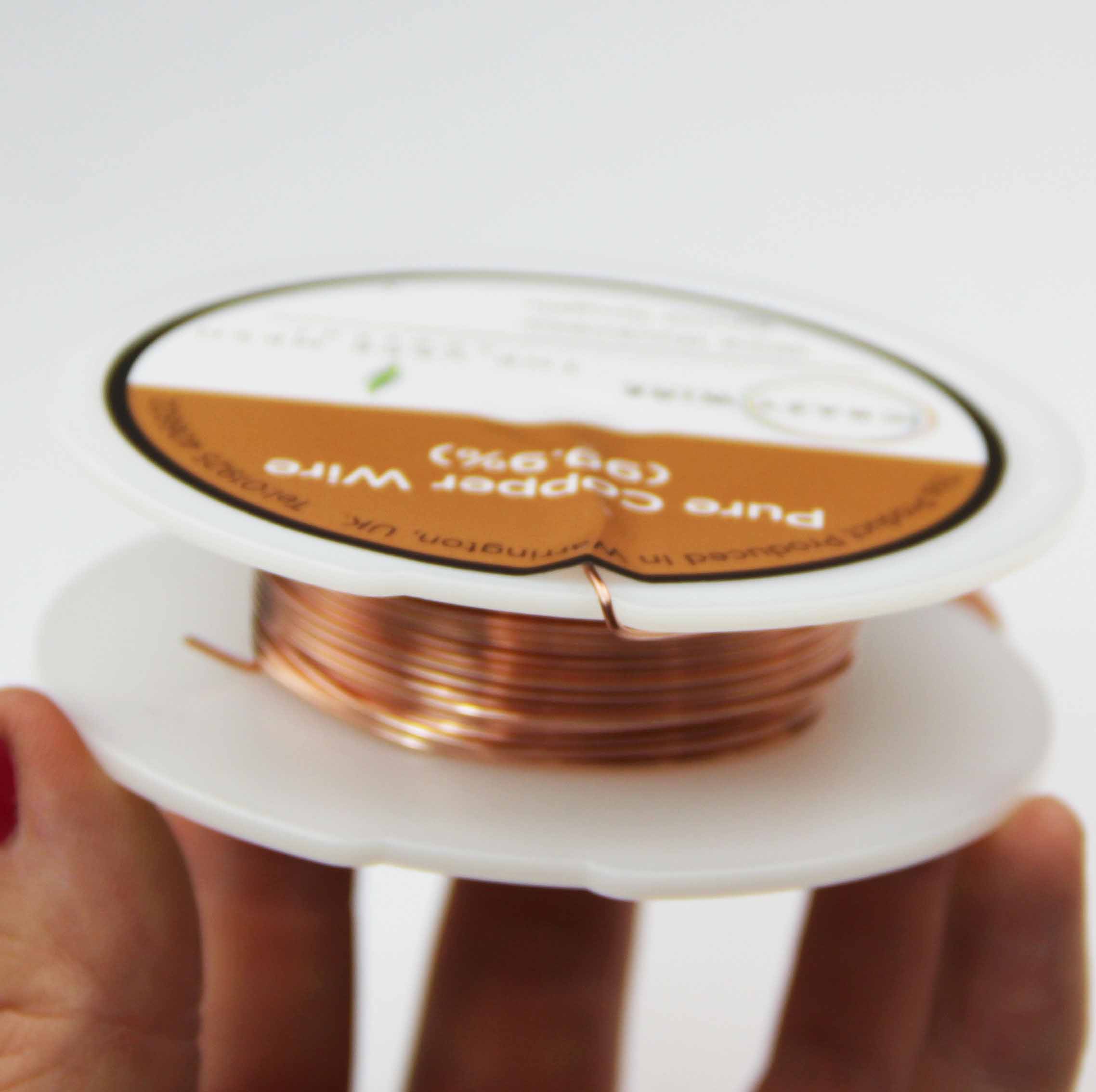
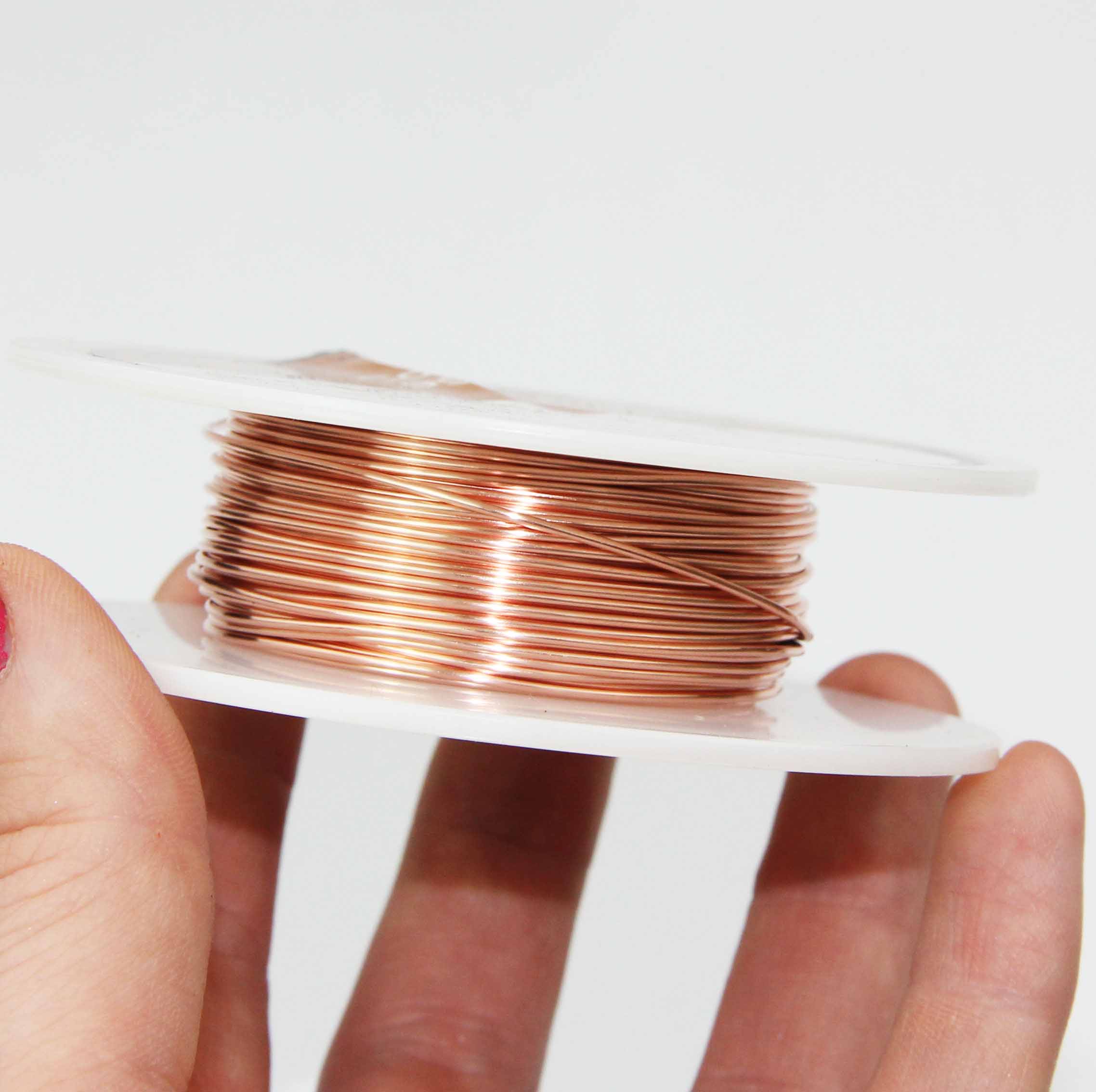
0.9mm Bare Copper Wires
The Crazy Wire Company are best know as suppliers of top-quality bare copper wires in many thicknesses. We have enormous stock levels at all times, as we use this wire to weave our woven mesh products.
0.9mm bare copper wire refers to a copper wire that has a diameter of 0.9 millimetres and has no insulation or coating on its surface. Copper wire is a type of electrical conductor made from copper metal. It is widely used in electrical and electronic applications because copper is an excellent conductor of electricity and has good mechanical properties. Copper wire comes in various sizes, shapes, and forms, and can be coated or insulated with different materials depending on the specific application.
Key product details:
- 99.9% Copper with the 0.01% being made up of trace elements.
- Assay – =99.9%
- Form – wire
- Resistivity – 1.673 µO-cm, 20°C
- Diam. – Various
- bp – 2567 °C(lit.)
- mp – 1083.4 °C(lit.)
- Density – 8.94 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.)
Other Available Copper Options
- 0.15mm – 35 AWG
- 0.18mm – 35 AWG
- 0.2mm – 32 AWG
- 0.25mm – 30 AWG
- 0.3mm – 29 AWG
- 0.35mm – 27 AWG
- 0.4mm – 26 AWG
- 0.5mm – 24 AWG
- 0.6mm – 22 AWG
- 0.7mm – 21 AWG
- 0.8mm – 20 AWG
- 0.9mm – 19 AWG
- 1mm – 18 AWG
- 20mm x 25mm Copper Adhesive Strip
- 30mm x 25mm Copper Adhesive Strip
Why Use The Crazy Wire Company
- Quality of products: The Crazy Wire Company always offer high-quality products that meet industry standards and customer expectations.
- Selection: We offer a wide variety of wire products and sizes to meet the diverse needs of our customers. We have more than 600 products available through our site and counting.
- Price: We always offer the best value possible. Our wires are available as part of our major weaving processes, so it is bought at the best possible rate.
- Availability: Our products are kept in house and are ready to ship immediately.
- Customer service: Our experienced staff help our customers feel confident in their purchases and provide assistance when required.
What Else Is Available?
We do not only offer copper round wire. We also have a huge range of KA1 and stainless steel round wire in stock at all times.
Ribbon wire and flat wire are stocked for immediate dispatch too.
FAQs About Copper Wire
Copper Wire Uses
Pure copper wire has many uses due to its excellent electrical conductivity, ductility, and resistance to corrosion. Some of the most common uses of pure copper wire include:
- Electrical wiring: Copper wire is used extensively in electrical wiring, both in residential and commercial buildings, as well as in electrical equipment such as motors and generators.
- Telecommunications: Copper wire is used in telephone and internet cables to transmit data and voice signals.
- Power transmission: Copper wire is used in power transmission lines to distribute electricity over long distances.
- Automotive: Copper wire is used in the automotive industry for wiring in cars and other vehicles.
- Electronics: Copper wire is used in electronic devices such as computers, televisions, and other household appliances.
- Construction: Copper wire is used in construction for grounding and lightning protection.
- Jewellery: Copper wire is used in jewellery making for creating intricate designs and shapes.
- Sculpture: Copper wire is a popular medium for creating sculptures because of its malleability, color and the ability to patina over time.
These are some of the main uses of pure copper wire, but it is also used in other applications such as medical equipment, aerospace, and industrial machinery.
How Do I Tell If Copper Wire Is Pure?
There are several ways to determine the purity of copper wire:
- Visual Inspection: Pure copper wire has a reddish-orange colour and is relatively shiny. If the wire has a duller or greyish appearance, it may be mixed with other metals or have a coating that is not copper.
- Conductivity test: Pure copper has a high electrical conductivity, so testing the wire’s conductivity can provide an indication of its purity. A pure copper wire should have a higher conductivity than a wire that is mixed with other metals.
- Chemical test: Copper wire can be tested with various chemicals to determine its purity. For example, nitric acid can be used to test for the presence of other metals, such as brass or bronze.
- X-Ray Fluorescence (XRF): This is an analytical technique that can measure the composition of a metal. A XRF spectrometer can quickly and accurately determine the exact composition of the copper wire. This is a reliable method but it’s not commonly used in a home setting.
It’s worth noting that, even if the wire is pure copper, it could be alloyed with other metals to improve its mechanical properties. It’s also worth noting that none of this test will give you the exact percentage of copper in the wire, just if it’s pure or not.
How Does Electricity Pass In Copper Wire?
Electricity passes through a copper wire as a result of the flow of electrons. Copper is a metal that has a large number of free electrons in its outermost energy level, which makes it an excellent conductor of electricity.
When an electric voltage is applied across a copper wire, the voltage causes the free electrons in the wire to start moving. The electrons move from one end of the wire to the other, creating a flow of electric current. The flow of current is due to the movement of electrons from one atom to another along the length of the wire.
The speed of the flow of electrons through the copper wire depends on the voltage applied across the wire and the resistance of the wire. The resistance of the wire is determined by its composition, size, and temperature. The resistance of the copper wire opposes the flow of current, but it is relatively low compared to other materials, which makes copper a good choice for electrical wiring and other electrical applications.
How Are Thin Copper Wires Made Without Breaking?
Thin copper wires are typically made using a process called wire drawing. Wire drawing is a process of reducing the diameter of a wire by pulling it through a die of smaller size. The wire drawing process can be performed either cold or hot, depending on the material and the desired outcome.
In the case of copper wire, cold drawing is often used to make thin wires because copper is a relatively ductile material that can be easily deformed without breaking. In a cold drawing process, a copper wire is fed through a series of progressively smaller dies, reducing its diameter with each pass. The wire is typically lubricated to reduce friction and prevent damage during the drawing process.
To prevent breaking during the wire drawing process, the wire is typically annealed, or heated and cooled, after each pass through the die. This process makes the wire more pliable and less likely to break as it is drawn through the smaller dies.
In some cases, intermediate annealing may be performed during the drawing process to ensure that the wire remains ductile and does not break. The wire is typically checked for quality after each drawing pass and may be rejected if it is found to be damaged or if the wire’s diameter is not within the desired tolerance.
Check out our blog ‘what you need to know about: pure copper wire’ for more information on copper wire in general. Our goal for our blogs and help guides is to answer as many questions as possible to help to explain the possibilities of mesh to our customers.
We also offer similar products through our highly popular eBay store, check us out there too.
Contact our team today if you have any questions at all. We are always really keen to help in any way that we can.









Reviews
There are no reviews yet.