Description
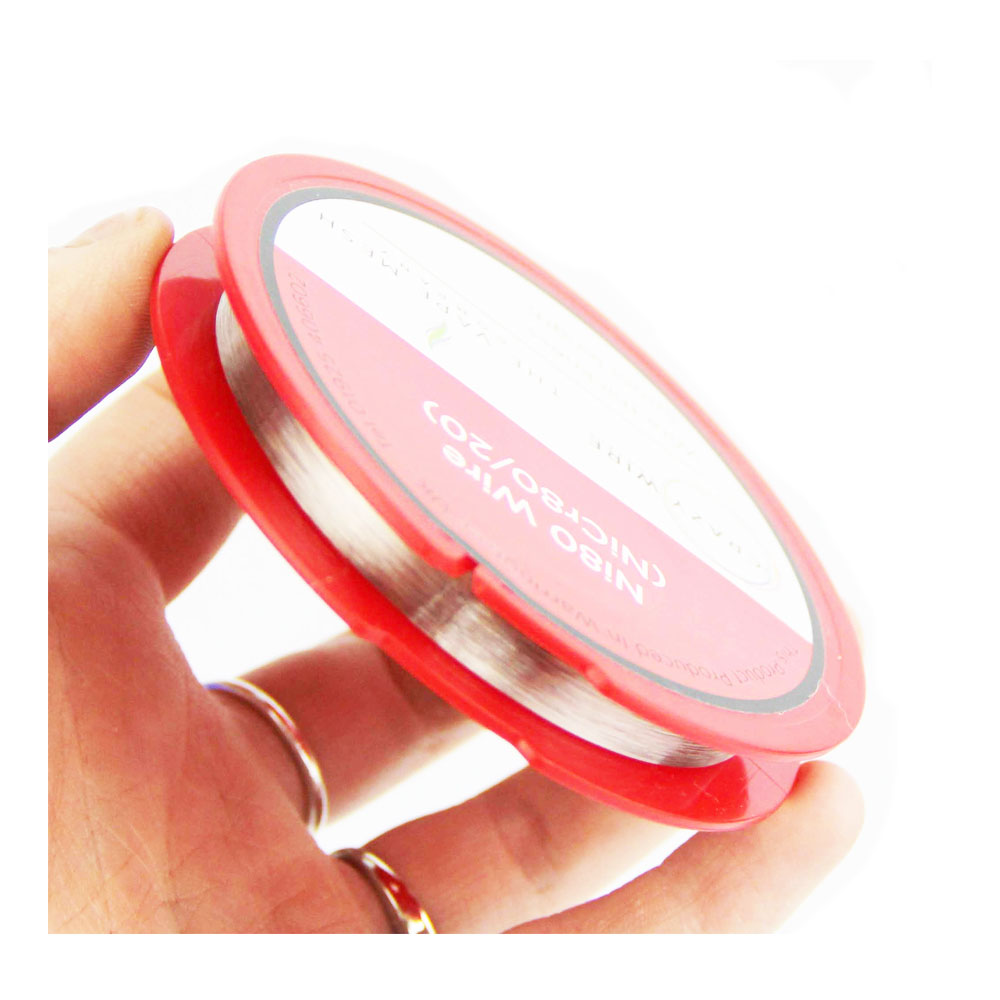
0.4mm Ni80 Heating Wire
The Crazy Wire Company are well known as suppliers of top quality Ni80 heating wire. We have enormous stock levels at all times, as we use this wire to weave our high specification woven mesh products. Our brilliant staff are experts in producing our spools of round wire on our 6 rapid action winding machines. All spools are produced to carry a little extra length to make up for any waste when handling the product.
The 0.4mm (26 AWG) Ni80 Nichrome heating wire is a high-quality alloy comprised of nickel and chromium, designed for efficient and consistent heating. In addition to its superior electrical resistance, this wire ensures even heat distribution throughout its length. In addition to its high temperature resistance, this material has a long lifespan due to its resistance to oxidation. The heating wire can be found in electric heaters, toasters, hair dryers, industrial furnaces, laboratory equipment, home appliances such as electric kettles and rice cookers, and specialised automotive and ceramic applications. With this heating wire, you can achieve a reliable heating solution for a variety of applications with both durability and performance.
The resistance of Nichrome 80 wire can be calculated using the formula:
R = ρ * L / A
Where:
R = resistance (Ω) ρ = resistivity of the wire material (Ωm) L = length of the wire (m) A = cross-sectional area of the wire (m^2)
The resistivity of Nichrome 80 is approximately 1.10 × 10^-6 Ωm. To use the formula, you will need to know the length of the wire and its cross-sectional area. The cross-sectional area can be calculated from the diameter of the wire using the formula:
A = (π/4) * d^2
Where:
d = diameter of the wire (m)
With a diameter of 0.4mm, the cross-sectional area of the wire would be approximately 0.000158 square millimetres.
Once you have the length and cross-sectional area of the wire, you can calculate the resistance of the 0.4mm Nichrome 80 wire by plugging these values into the formula.
Key product details:
- Diameter – 0.4mm (400 Micron – 26 AWG)
- Ohms/m – 8.71
- Technical Specification:
- Ni – Rest
- Cr – 20.0 – 23.0
- Fe – <1.0
- Max Continuous Service Temp Of Element – 1200
- Micrographic Structure – Austenite
- Magnetic Properties – Nonmagnetic
- Electrical resistance is high
- Corrosion resistance is high
Why Use The Crazy Wire Company
- Quality of products: The Crazy Wire Company always offer high-quality products that meet industry standards and customer expectations.
- Selection: We offer a wide variety of wire products and sizes to meet the diverse needs of our customers. We have more than 600 products available through our site and counting.
- Price: We always offer the best value possible. Our wires are available as part of our major weaving processes, so it is bought at the best possible rate.
- Availability: Our products are kept in house and are ready to ship immediately.
- Customer service: Our experienced staff help our customers feel confident in their purchases and provide assistance when required.
What Else Is Available?
We do not only offer Ni80 round wire. We also have a huge range of KA1 and stainless steel round wire in immediate stock too.
Ribbon wire and flat wire are stocked for immediate dispatch too.
FAQs About This Wire
Why Heat Wire?
Heat wire, also known as resistance wire, is used to generate heat through electrical resistance. When an electrical current is passed through a resistance wire, the wire heats up due to the resistance of the material to the flow of electrical current. This resistance causes the electrons to collide with each other and with the atoms of the wire. This releases energy in the form of heat.
Heat wire is commonly used in a variety of applications, including:
- Heating elements: Heat wire is used as the heating element in appliances such as electric heaters, toasters, and furnaces.
- Temperature control: Heat wire is used in temperature control systems, such as those found in automobiles and HVAC systems. This is to regulate the temperature of a specific area.
- Medical devices: Heat wire is used in medical devices, such as heat pads and heating blankets, to provide warmth and comfort to patients.
- Process heating: Heat wire is used in industrial processes to heat materials or substances for various purposes, such as melting, welding, or drying.
- Research and development: Heat wire is used in scientific and engineering research to study the effects of heat on materials and systems.
Heat wire is a versatile material that can be used in a variety of heating applications. This is due to its ability to generate heat through electrical resistance, its reliability and durability, and its relatively low cost.
Which Heating Wire?
The choice of heating wire will depend on several factors, including:
- Operating temperature: The heating wire must be able to withstand the temperatures encountered in the specific heating application. It’s important to choose a wire with a high maximum operating temperature.
- Resistance: The resistance of the wire will affect the amount of heat generated, so it’s important to choose a wire with the correct resistance for the specific heating application.
- Durability: The heating wire must be able to withstand the conditions of the specific heating application, such as exposure to corrosive materials. It’s important to choose a wire that is durable and long-lasting.
- Cost: The cost of the wire can be a significant factor in the choice of material, so it’s important to consider the cost-effectiveness of different options.
- Availability: Some wire materials may not be readily available in certain regions, so it’s important to consider the availability of the material.
Based on these factors, common choices for heating wire include FeCrAl alloys, Nichrome 80, and KA1. FeCrAl alloys are a common choice due to their high resistance, high maximum operating temperature, and durability. Nichrome 80 is another commonly used material due to its relatively high resistance, ability to withstand high temperatures, and relatively low cost. KA1 is a type of iron-chromium-aluminium alloy that is also commonly used for heating wire due to its high resistance, high maximum operating temperature, and durability.
Can Heating Element Be Replaced?
Yes, heating elements can be replaced in many cases. The heating element is a crucial component of many heating appliances. It is responsible for converting electrical energy into heat. If the heating element is not working properly, it may cause the appliance to not heat up effectively, or to heat unevenly. In these cases, replacing the heating element can help restore proper function to the appliance.
The process of replacing a heating element can vary depending on the type of appliance and the location of the heating element. In some cases, the heating element may be located in a readily accessible area and can be easily replaced. In other cases, the heating element may be located in a more complex or difficult to access location, and may require professional repair services to replace.
It’s important to keep in mind that while replacing a heating element may resolve heating issues with an appliance, there may be other underlying problems that are causing the heating element to fail. Before replacing the heating element, it may be necessary to diagnose the root cause of the problem to ensure that the new heating element is not subjected to the same conditions that caused the previous element to fail.
Can Heating Element Burn?
Yes, a heating element can burn out or overheat if it is subjected to conditions that are beyond its capabilities. The heating element works by converting electrical energy into heat, and if too much current is flowing through the element, it can overheat and become damaged. This can cause the element to burn out, become brittle, or even break.
Some common reasons for heating element burnout or overheating include:
- Overloading: If too much electrical current is flowing through the heating element, it can overheat and become damaged. This can occur if the appliance is used for longer than recommended, or if it is used to heat a large volume of material.
- Improper wiring: If the heating element is not properly wired, it can be subjected to an improper voltage or current. This can cause it to overheat and become damaged.
- Ambient temperature: If the heating element is located in an environment that is too hot, it can overheat and become damaged. This can occur if the heating element is located near another heat source, or if it is in a location that does not allow for proper air flow.
- Poor quality: If the heating element is made from poor quality materials, it can be more likely to overheat and become damaged. This can occur if the element is made from materials that are not suitable for high temperature applications. Also, if it is made from materials that are not properly treated to withstand high temperatures.
Check out our blog ‘what is nichrome‘ for more information on ni80 wire in general. Our goal for our blogs and help guides is to answer as many questions as possible to help to explain the possibilities of mesh to our customers.
We also offer similar products through our highly popular eBay store, check us out there too.
Contact our team today if you have any questions at all. We are always really keen to help in any way that we can.