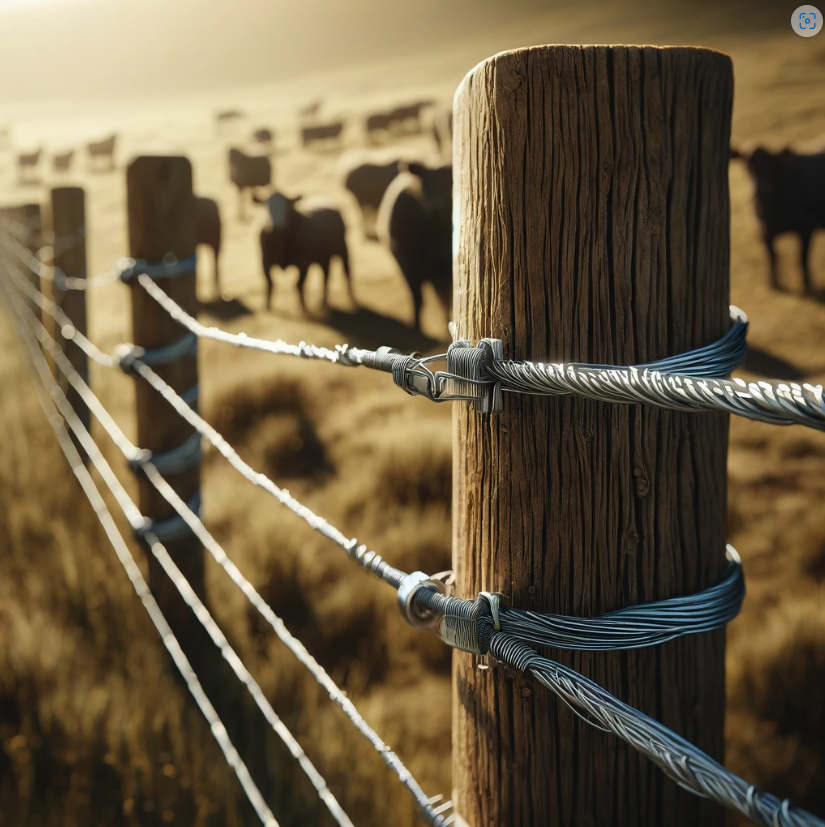
Galvanised tension wiring is a staple in various industries, prized for its strength, durability, and resistance to corrosion. But when it comes to marine environments, a question often arises: Can galvanised tension wire withstand harsh, salt-laden conditions? In this blog post, we will examine galvanised tension wire, its properties, and how it performs in marine environments. It is our goal to provide you with a thorough understanding so that you can make an informed decision.
Understanding Galvanised Tension Wiring
What is Galvanised Tension Wiring?
Galvanised tension wiring is essentially steel wire that has been coated with a layer of zinc to enhance its durability and resistance to corrosion. The galvanisation process involves dipping the steel wire into molten zinc, which forms a protective layer on the surface. This zinc coating acts as a barrier, preventing the steel underneath from rusting and corroding when exposed to moisture and other environmental factors.
Types of Galvanisation
There are two primary types of galvanisation used for tension wiring:
- Hot-Dip Galvanisation: This involves immersing the steel wire in molten zinc, resulting in a thick, robust coating. Hot-dip galvanised wire is highly resistant to abrasion and corrosion.
- Electro-Galvanisation: In this process, the steel wire is coated with zinc through an electroplating technique. While this method provides a smoother finish and more precise control over coating thickness, the resulting zinc layer is typically thinner compared to hot-dip galvanisation.
Properties of Galvanised Tension Wiring
Corrosion Resistance
The primary advantage of galvanised tension wiring is its enhanced corrosion resistance. The zinc coating acts as a sacrificial layer, corroding before the underlying steel does. This is especially important in environments where moisture is prevalent.
Strength and Durability
Galvanised tension wires maintain the inherent strength of steel while adding the protective benefits of zinc. This makes them suitable for applications requiring high tensile strength and durability.
Cost-Effectiveness
Compared to stainless steel and other corrosion-resistant materials, galvanised tension wiring offers a cost-effective solution. The galvanisation process adds significant protection without substantially increasing the cost.

Marine Environments: Challenges and Considerations
Saltwater Corrosion
Marine environments are particularly harsh due to the presence of saltwater, which accelerates corrosion processes. Saltwater contains chloride ions that can penetrate protective coatings and cause rapid deterioration of the underlying metal.
Humidity and Moisture
High humidity levels and constant exposure to moisture further exacerbate corrosion in marine environments. This continuous exposure to water can test the limits of any protective coating.
Temperature Fluctuations
Marine environments often experience significant temperature fluctuations, which can cause materials to expand and contract. This thermal cycling can lead to the formation of micro-cracks in protective coatings, allowing corrosive elements to penetrate.
Galvanised Tension Wiring in Marine Environments
Performance of Galvanised Tension Wiring
When considering galvanised tension wiring for marine environments, it’s essential to evaluate its performance under these specific conditions.
Zinc Coating Thickness: The thickness of the zinc coating is a critical factor. Hot-dip galvanised tension wiring, with its thicker zinc layer, generally offers better protection compared to electro-galvanised alternatives. The thicker the zinc coating, the longer it can withstand the corrosive effects of saltwater.
Sacrificial Protection: The zinc coating provides sacrificial protection. Even if the coating is breached, the surrounding zinc will corrode preferentially, protecting the steel underneath. However, in a marine environment, this sacrificial layer can be consumed more rapidly than in less corrosive environments.
Longevity and Maintenance: While galvanised tension wiring can perform well in marine environments, its longevity may be reduced compared to less aggressive settings. Regular inspection and maintenance are crucial to identify areas where the coating has worn away and to reapply protective measures as needed.
Enhancing the Performance of Galvanised Tension Wiring
Additional Protective Coatings
To extend the lifespan of galvanised tension wire in marine environments, additional protective coatings can be applied. These can include:
- Polymer Coatings: Applying a polymer layer over the galvanised coating can provide an extra barrier against moisture and salt.
- Paints and Sealants: Specialised marine-grade paints and sealants can be used to cover the galvanised wire, offering additional protection and reducing direct exposure to the elements.
Regular Maintenance
Implementing a regular maintenance schedule is essential for galvanised tension wiring used in marine environments. This includes:
- Inspection: Regularly inspecting the wiring for signs of corrosion or damage.
- Cleaning: Removing salt deposits and other corrosive substances that may accumulate on the wire.
- Reapplication of Coatings: Periodically reapplying protective coatings to areas where the original zinc layer has worn thin.

Alternatives to Galvanised Tension Wiring
Stainless Steel Tension Wiring
For those seeking an alternative to galvanised tensioning wire, stainless steel is a common choice. Stainless steel offers excellent corrosion resistance, even in harsh marine environments, due to its chromium content, which forms a passive oxide layer on the surface.
Polyethylene-Coated Tension Wiring
Another option is tension wiring coated with polyethylene or other durable polymers. These coatings can provide superior protection against saltwater and UV radiation, making them suitable for marine applications.
Case Studies and Real-World Applications
Marinas and Harbors
In marinas and harbors, galvanised tension wiring is often used for securing boats and docks. While it performs adequately with proper maintenance, many facilities opt for additional coatings or switch to stainless steel for increased longevity.
Fishing Industry
The fishing industry relies heavily on tension wiring for nets and traps. Galvanised tension wiring is commonly used, but frequent exposure to saltwater necessitates regular maintenance and, in some cases, the use of alternative materials.
Coastal Construction
In coastal construction, such as building piers and sea defenses, galvanised tensioning wire is used for reinforcement. Here, the addition of protective coatings and strict maintenance protocols are critical to ensuring the integrity of the structures.
To conclude, galvanised tension wiring can be used in marine environments, but its suitability depends on some factors, including the zinc coating thickness, additional protective measures, and rigorous maintenance procedures. While galvanised tension wiring offers good corrosion resistance, it may not provide the same level of long-term performance as stainless steel or other specialised materials designed for marine applications.
For those considering galvanised tension wire in marine applications, it is advisable to:
- Opt for hot-dip galvanised wire with a thicker zinc coating.
- Apply additional protective coatings to enhance corrosion resistance.
- Establish a regular maintenance schedule to monitor and address any signs of corrosion promptly.
By taking these steps, galvanised tension wiring can serve effectively in marine environments, balancing performance and cost-efficiency.
We offer also a massive range of stainless steel wire and nichrome wire through our store. Choose the wire that you want to work with and we’ll get spooling.
If you’re interested in learning more about wire, check out our other blog on Everything You Need to Know About Wires.
We are also proud to supply this product on our highly popular eBay store, check us out there too.
Thank you for checking out our site.

Nichrome Wire Safety: Top Tips for Working Safely

Best Wire for Electronics Projects

Is Ni80 Wire Suitable for DIY Heating Elements

Wire Grades Explained

How Wire Diameter Affects Strength and Flexibility

How to Cut and Shape Wire for Custom Applications

Can Wire Be Used in 3D Printing?

How Wire Composition Affects Conductivity