Stainless steel, renowned for its strength, durability, and corrosion resistance, has become a cornerstone in modern manufacturing and construction.
Its versatility is evident in its widespread use across industries – from the intricate workings of medical devices to the robust structure of architectural frameworks.
In this article, we focus on two specific grades of stainless wire: 316 and 430. Each has unique properties and common applications, making them integral in different sectors. Understanding the differences between these grades is essential for professionals in engineering, construction, and design, ensuring the right material is chosen for the right application.
Let’s get into it…
Understanding Stainless Steel
In addition to its remarkable resistance to corrosion, heat, and chemical damage, stainless steel is an iron alloy. A passive layer of chromium oxide forms on steel’s surface, protecting it from various environmental factors, primarily due to the presence of chromium. The strength and ductility of stainless steel allow it to be formed into a variety of shapes and sizes without losing its integrity.
The versatility of stainless steel makes it an ideal material for numerous applications. Due to its ability to withstand extreme environments and maintain structural integrity under high stress, it is indispensable in the construction, automotive, aerospace, and marine industries. Furthermore, its hygienic properties and ease of cleaning contribute to its popularity in medical, food processing, and kitchen applications.
Overview of 316 Grade Stainless Wire
In comparison to most other stainless steel grades, 316 grade stainless wire is known for its enhanced corrosion resistance. In part, this is due to its composition, which is made up of chromium, nickel, and molybdenum. With its molybdenum content, 316 stainless wire is highly resistant to chlorides and acidic substances.
In saltwater and acidic conditions, 316 grade stainless wire is commonly used in marine environments, chemical processing equipment, and medical devices. Due to its ability to withstand these conditions without degrading, it is an excellent choice for applications that require longevity and reliability.

Overview of 430 Grade Stainless Wire
The 430 grade stainless wire, on the other hand, is a ferritic alloy known for its corrosion resistance and formability. Due to its higher chromium content and lack of nickel, it is less expensive than 316 grade. In certain applications, its magnetic properties are useful, and it is resistant to nitric acid and organic acids.
For its aesthetic appeal and ability to withstand moderately aggressive environments, 430 grade stainless wire is commonly used in appliances, automotive trim, and interior architectural features. Magnetic properties also make it suitable for specific electronic and magnetic applications.
Key Differences Between 316 and 430
The main differences between 316 grade stainless wire and 430 grade stainless wire can be attributed to their composition, which directly affects their corrosion resistance, their durability, and their suitability for use in various environments.
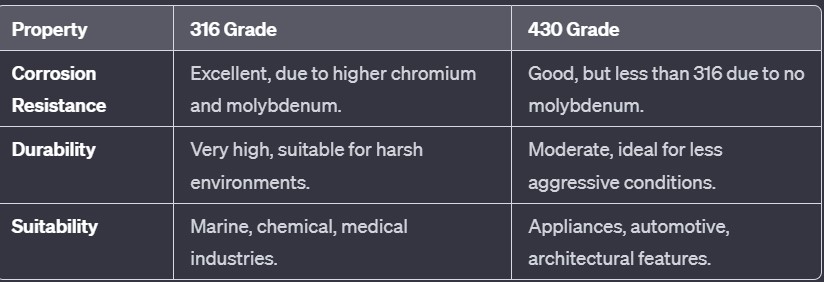
Due to its superior corrosion resistance, 316 grade stainless steel is more appropriate for environments with a high level of chloride exposure or an acidic environment. In contrast, the 430 grade is suitable for less corrosive environments and is preferred for its aesthetic qualities in architectural and appliance applications due to its low corrosion resistance.
Practical Applications
In practical terms, the choice between 316 and 430 grade stainless wire often depends on the specific demands of the application:
- 316 Grade: Known for its saltwater corrosion resistance, its non-reactivity, and its strength in acidic environments, it is often used in marine applications, medical devices, and chemical processing plants.
- 430 Grade: It is commonly used in automotive trims due to its aesthetic appeal and moderate corrosion resistance, in kitchen appliances due to its good formability, and in interior architectural elements due to its magnetic properties.
The decision between these two grades hinges on environmental factors, aesthetic considerations, and the specific requirements of strength and corrosion resistance.
Cost Analysis
In terms of cost, 430 grade stainless wire is generally more affordable than 316 due to the absence of nickel and molybdenum. However, the upfront cost is just one aspect of the overall cost-effectiveness:
- 316 Grade: In harsh environments where replacement or maintenance is frequent, its durability and corrosion resistance can lead to lower long-term costs.
- 430 Grade: Provides a cost-effective solution for applications that do not require the superior corrosion resistance of stainless steel 316. This makes it a practical choice for environments that are less aggressive or indoors.
Maintenance and Longevity
Maintaining the quality and extending the lifespan of both 316 and 430 grade stainless wires involve several key practices:
- Regular Cleaning: Cleaning with mild detergent and water on a regular basis is one of the best ways to remove contaminants that can cause corrosion.
- Inspection: Inspections should be carried out periodically to detect signs of wear and damage, especially in harsh environments where 316 grade is used.
- Protective Coatings: There are various ways to enhance corrosion resistance, particularly for 430 grade steel in more challenging environments, by applying protective coatings or treatments.
- Environmental Consideration: You should store and use 430 grade in a corrosive-free environment – avoid exposing it to highly corrosive environments.
Both grades require proper maintenance in order to function properly. In spite of the fact that 316 grade offers superior durability and corrosion resistance, neglect can still lead to premature degradation of the metal. It should be noted, on the other hand, that well-maintained 430 grade steel can have an amazingly long service life, even under moderately challenging conditions.
Choosing the Right Grade for Your Needs
Selecting the appropriate grade of stainless wire is a critical decision that depends on several key factors:
Environmental Exposure: It is important to consider the environmental conditions in which the wire will be exposed. When exposed to environments with high chloride levels, such as coastal areas, or when the wire will be exposed to chemicals such as acids and alkalis, the 316 grade is recommended due to its superior corrosion resistance. It is often sufficient to use 430 grade steel for indoor applications or environments that are less corrosive.
Budget Constraints: Even though 316 grade is generally more expensive, its longevity in harsh environments may provide a better value over the long term. In other cases, if budget constraints are the primary concern and the environmental conditions aren’t as demanding, 430 grade might be a cost-effective option for your application.
Intended Use: Think about the specific application of the wire. 316 grade wire is more suitable to be used in applications where strength and resistance to high temperatures are paramount, such as in heavy industry and construction, where strength and resistance to high temperatures are of paramount importance. The 430 grade of stainless steel is often adequate for the less demanding applications, such as decorative items or certain automotive applications.
Based on these factors, you will be able to determine which grade of stainless wire is best suited to your needs. If you understand the unique attributes of each grade, you will be able to choose a material that will fit your budget and perform effectively in its intended environment.
In this article, we have discussed 316 and 430 grade stainless wire’s distinct characteristics, applications, and comparative merits. Due to its superior corrosion resistance and durability, 316 grade is ideal for harsh environmental conditions and demanding industrial applications. However, 430 grade offers a more cost-effective solution for less aggressive environments, with adequate corrosion resistance and a variety of aesthetic and practical uses.
Environmental exposure, budgetary considerations, and the specific requirements of the intended application should all be taken into account when choosing between these two grades. For informed decisions, it is essential to understand these differences, ensuring that the chosen material meets both your project’s performance and budgetary constraints.
In construction, manufacturing, or design, you can ensure the longevity, functionality, and cost-effectiveness of your projects by choosing the right grade of stainless wire. It is important to remember that the right material not only performs well under the given conditions, but also offers the best return on investment in the long term.
We offer also a massive range of stainless steel wire and nichrome wire through our store. Choose the wire that you want to work with and we’ll get spooling.
If you’re interested in learning more about wire, check out our other blog on Everything You Need to Know About Wires.
We are also proud to supply this product on our highly popular eBay store, check us out there too.
Thank you for checking out our site.

Nichrome Wire Safety: Top Tips for Working Safely

Best Wire for Electronics Projects

Is Ni80 Wire Suitable for DIY Heating Elements

Wire Grades Explained

How Wire Diameter Affects Strength and Flexibility

How to Cut and Shape Wire for Custom Applications

Can Wire Be Used in 3D Printing?

How Wire Composition Affects Conductivity