Description
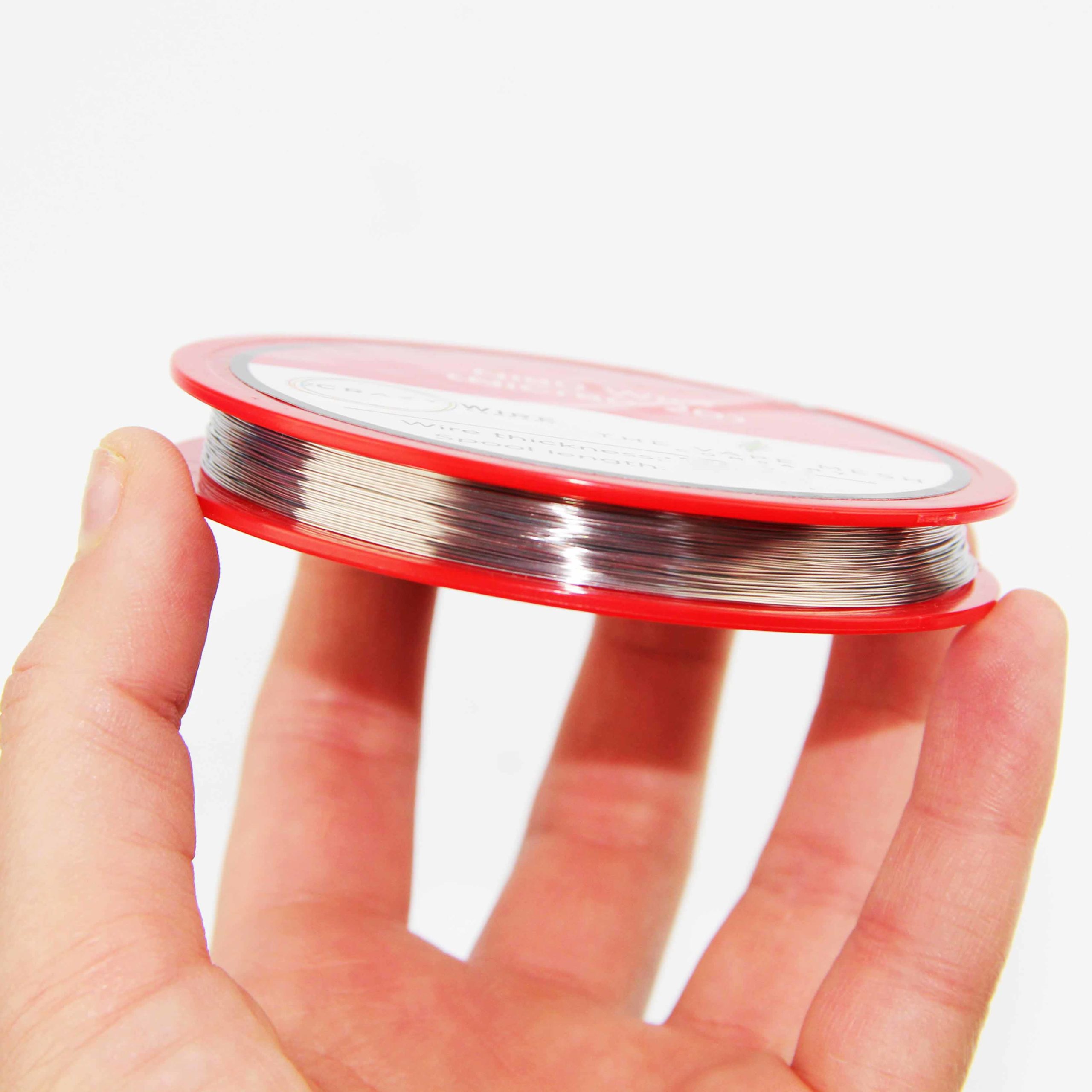
0.25mm Ni80 Electric Resistance Wire
The Crazy Wire Company are well known as suppliers of top quality Ni80 electric resistance wire. We have enormous stock levels at all times, as we use this wire to weave our high specification woven mesh products. Our brilliant staff are experts in producing our spools of round wire on our 6 rapid action winding machines. All spools are produced to carry a little extra length to make up for any waste when handling the product.
The 0.25mm (30 AWG) Ni80 nichrome electric resistance wire is a high-quality alloy of nickel and chromium. It’s known for its consistent electrical conductivity and superior heat resistance. Its electric resistance properties make it a top choice for heating elements, resistors, and electric circuits in industrial and household applications. In spite of challenging environments, it promises longevity because of its corrosion resistance. Professional or home projects, this wire delivers precision, durability, and reliable performance, addressing a wide range of electrical and heating needs.
Nichrome wire is a type of resistance wire made of an alloy of nickel and chromium, which is known for its high resistance and resistance to oxidation at high temperatures. 0.25mm Nichrome wire is a relatively thin wire. It can be used in a variety of heating and electrical applications, including hot cutting of certain materials.
Key product details:
- Diameter – 0.25mm (250 Micron – 30 AWG)
- Ohms/m – 21.94
- Technical Specification:
- Ni – Rest
- Cr – 20.0 – 23.0
- Fe – <1.0
- Max Continuous Service Temp Of Element – 1200
- Micrographic Structure – Austenite
- Magnetic Properties – Nonmagnetic
- Electrical resistance is high
- Corrosion resistance is high
Why Use The Crazy Wire Company
- Quality of products: The Crazy Wire Company always offer high-quality products that meet industry standards and customer expectations.
- Selection: We offer a wide variety of wire products and sizes to meet the diverse needs of our customers. We have more than 600 products available through our site and counting.
- Price: We always offer the best value possible. Our wires are available as part of our major weaving processes, so it is bought at the best possible rate.
- Availability: Our products are kept in house and are ready to ship immediately.
- Customer service: Our experienced staff help our customers feel confident in their purchases and provide assistance when required.
What Else Is Available?
We do not only offer Ni80 round wire. We also have a huge range of KA1 and stainless steel round wire in immediate stock too.
Ribbon wire and flat wire are stocked for immediate dispatch too.
FAQs About This Wire
What Causes Resistance In A Wire?
Resistance in a wire is caused by the collision of electrons with atoms in the wire material. When an electrical current flows through a wire, the electrons move through the material and collide with the atoms, which impedes their flow. This collision of electrons with atoms results in resistance to the flow of electrical current.
The resistance of a wire depends on several factors, including the material of the wire, its cross-sectional area, length, temperature, and the presence of a magnetic field. Different materials have different resistivities, which is a measure of how strongly a material resists the flow of electrical current. The resistance of a wire is directly proportional to its length and inversely proportional to its cross-sectional area.
Additionally, temperature can affect the resistance of a wire, with higher temperatures typically leading to higher resistance. This is because the increase in temperature can cause the atoms in the wire to vibrate more, leading to more collisions between electrons and atoms and thus higher resistance.
What Affects Resistance In A Wire?
The resistance in a wire is affected by several factors, including:
Material: The material of the wire, including its composition and structure, will affect its resistance. Different materials have different resistivities, which is a measure of how strongly a material resists the flow of electrical current. For example, pure copper has a low resistivity, which means it has low resistance, while Nichrome, a commonly used resistance wire, has a much higher resistivity and higher resistance.
Wire cross-sectional area: The cross-sectional area of the wire, or its diameter, is directly proportional to its resistance. A larger cross-sectional area means lower resistance, while a smaller cross-sectional area means higher resistance.
Length: The length of the wire is directly proportional to its resistance. A longer wire will have higher resistance than a shorter wire of the same cross-sectional area and material.
Temperature: The temperature of the wire will affect its resistance, with higher temperatures typically leading to higher resistance. The relationship between temperature and resistance is known as the temperature coefficient of resistance.
Magnetic field: The presence of a magnetic field can affect the resistance of a wire, especially if the wire is made of a material with a high magnetic susceptibility, such as some types of iron and steel.
By understanding the factors that affect resistance in a wire, engineers and designers can choose the appropriate type and size of wire for a specific application, taking into account the desired resistance, the electrical current to be carried, and other requirements.
Best Low Resistance Wire
The best low resistance wire will depend on the specific requirements of the application. Some common low resistance wire materials include:
Copper: Copper is one of the most widely used low resistance wire materials due to its low resistivity, good conductivity, and resistance to corrosion. Copper wire is often used in electrical wiring, power transmission, and other applications that require low resistance and high conductivity.
Silver: Silver has a lower resistivity than copper and is therefore a more conductive material, making it one of the best low resistance wire materials. However, silver is more expensive than copper and is more susceptible to corrosion, so it is not as widely used.
Aluminium: Aluminium is a lightweight and relatively low resistance wire material that is widely used in electrical wiring and power transmission applications. Aluminum has a lower resistivity than copper and is therefore a more conductive material, but it is also more prone to corrosion.
Gold: Gold has a very low resistivity and is an excellent conductor, making it one of the best low resistance wire materials.
Electric Resistance Of Wire Formula
The electric resistance of a wire can be calculated using Ohm’s law, which states that the resistance of a wire (R) is equal to the voltage across the wire (V) divided by the current through the wire (I), or R = V/I.
Another formula for the resistance of a wire is given by the equation R = ρ * L / A, where ρ is the resistivity of the material, L is the length of the wire, and A is the cross-sectional area of the wire. The resistivity is a measure of how strongly a material resists the flow of electrical current, and it is a property of the material that is independent of the wire’s shape or size.
To calculate the resistance of a wire using the formula R = ρ * L / A, you need to know the resistivity of the wire material, the length of the wire, and its cross-sectional area. Once you have these values, you can plug them into the equation and solve for the resistance of the wire.
Check out our blog ‘what is nichrome‘ for more information on ni80 wire in general. Our goal for our blogs and help guides is to answer as many questions as possible to help to explain the possibilities of mesh to our customers.
We also offer similar products through our highly popular eBay store, check us out there too.
Contact our team today if you have any questions at all. We are always really keen to help in any way that we can.