Description
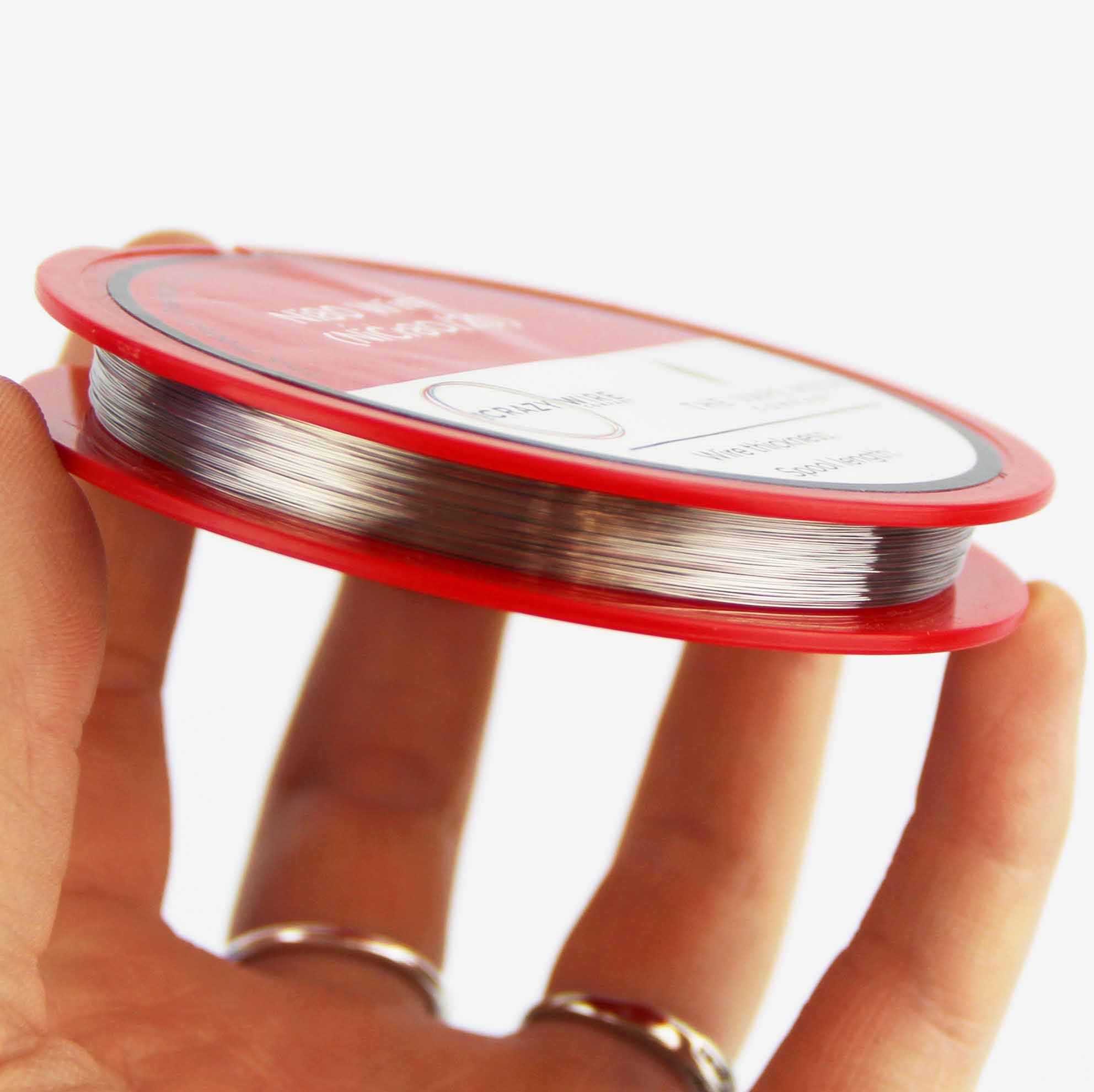
0.18mm Ni80 Hot Wire Cutting
The Crazy Wire Company are well known as suppliers of top quality Ni80 hot wire cutting wire. We have enormous stock levels at all times, as we use this wire to weave our high specification woven mesh products. Our brilliant staff are experts in producing our spools of round wire on our 6 rapid action winding machines. All spools are produced to carry a little extra length to make up for any waste when handling the product.
The NiCr 80/20 hot wire cutting tool has a diameter of 0.18mm (33 AWG) and is made from NiCr and features high precision and durability. Due to its 80% Nickel and 20% Chromium composition, it offers excellent heat resistance. This makes it an excellent choice for a wide range of applications. As a result of its slender diameter, it ensures precise cuts, which are ideal for detailed tasks. The metal is highly valued in electronics for its accuracy, and it’s also used in aerospace, automotive, craft, and architectural projects because of its adaptability. The consistency of its temperature makes it ideal for laboratory settings with consistent heating requirements.
Nichrome wire is an alloy of nickel, chromium, and sometimes iron, that is commonly used as a heating element. With a diameter of 0.18mm, the nichrome wire would be considered thin and would likely have a relatively low resistance. This makes it suitable for use in applications where a heating element with low power consumption is desired.
Key product details:
- Diameter – 0.18mm (180 Micron – 33 AWG)
- Ohms/m – 42.83
- Technical Specification:
- Ni – Rest
- Cr – 20.0 – 23.0
- Fe – <1.0
- Max Continuous Service Temp Of Element – 1200
- Micrographic Structure – Austenite
- Magnetic Properties – Nonmagnetic
- Electrical resistance is high
- Corrosion resistance is high
Why Use The Crazy Wire Company
- Quality of products: The Crazy Wire Company always offer high-quality products that meet industry standards and customer expectations.
- Selection: We offer a wide variety of wire products and sizes to meet the diverse needs of our customers. We have more than 600 products available through our site and counting.
- Price: We always offer the best value possible. Our wires are available as part of our major weaving processes, so it is bought at the best possible rate.
- Availability: Our products are kept in house and are ready to ship immediately.
- Customer service: Our experienced staff help our customers feel confident in their purchases and provide assistance when required.
What Else Is Available?
We do not only offer Ni80 round wire. We also have a huge range of KA1 and stainless steel round wire in immediate stock too.
Ribbon wire and flat wire are stocked for immediate dispatch too.
FAQs About This Wire
What Causes High Resistance In A Wire?
There are several factors that can cause high resistance in a wire:
Material Properties: The type of material used to make the wire can impact its resistance. For example, metals with a high resistivity, such as gold or silver, will have higher resistance than those with low resistivity, such as copper or aluminum.
Diameter: The diameter of the wire also affects its resistance. Thinner wires have a higher resistance compared to thicker wires because there is less cross-sectional area for electrons to flow through.
Length: The longer the wire, the greater its resistance. This is because the electrons have further to travel, which increases the chance of collisions and energy loss along the way.
Temperature: As the temperature of the wire increases, so does its resistance. This is because the increased heat causes the atoms in the wire to vibrate more, which increases the chance of collisions between electrons and atoms.
Impurities: Impurities in the wire, such as contaminants or manufacturing defects, can increase the resistance of the wire. This is because impurities can obstruct the flow of electrons and create additional resistance.
What Are The Different Types Of Resistance Wires?
There are several types of resistance wires that are used for different applications, including:
- Nichrome: This is a nickel-chromium alloy that is commonly used as a heating element in appliances, such as toasters, hair dryers, and water heaters. Nichrome has a high resistance and a high melting point, making it well-suited for these types of applications.
- KA1: This is another type of nickel-chromium alloy that is commonly used as a heating element. KA1 is often used in high-temperature applications, such as furnace heating elements, and is known for its stability and resistance to oxidation.
- Constantan: This is a copper-nickel alloy that is commonly used in temperature-sensing applications, such as thermocouples. Constantan has a low temperature coefficient of resistance, which means that its resistance changes very little with temperature.
- Manganin: This is a copper-manganese-nickel alloy that is also commonly used in temperature-sensing applications. Manganin has a low temperature coefficient of resistance and a low thermal expansion coefficient, making it well-suited for use in precise temperature measurements.
- Tungsten: This is a heavy metal that is commonly used as a resistance wire in high-temperature, high-power applications, such as in the filaments of incandescent light bulbs. Tungsten has a high melting point and a high resistance, making it well-suited for these types of applications.
These are some of the most common types of resistance wires, but there are many other alloys and materials that can be used depending on the specific requirements of an application.
What Is The Resistance Of Wires In A Heater At Room Temp?
The resistance of a wire in a heater depends on several factors, including the material the wire is made of, its length, and its cross-sectional area. At room temperature (usually considered to be around 20-25°C), the resistance of a wire can be calculated using Ohm’s law, which states that the resistance (R) of a conductor is equal to the voltage (V) across it divided by the current (I) flowing through it: R = V/I.
For a given material, the resistance of a wire is proportional to its length and inversely proportional to its cross-sectional area. As such, longer and/or thinner wires will have a higher resistance than shorter and/or thicker wires. The specific resistance of a material can vary, with metals like copper and aluminum having lower resistances than other materials like steel.
Do All Wires Have The Same Resistance?
No, not all wires have the same resistance. The resistance of a wire depends on several factors, including the material the wire is made of, its length, and its cross-sectional area. Different materials have different electrical resistivities, and as a result, will have different resistances for the same wire dimensions. For example, copper and aluminum are commonly used for electrical wiring due to their low electrical resistivity, whereas other materials like steel have a higher electrical resistivity and therefore higher resistance.
Additionally, the length of a wire affects its resistance. All other factors being equal, a longer wire will have a higher resistance than a shorter wire. The cross-sectional area of a wire also plays a role in its resistance. A wire with a larger cross-sectional area will have a lower resistance than a wire with a smaller cross-sectional area, since a larger wire can carry more electrical current with less voltage drop.
Check out our blog ‘what is nichrome‘ for more information on ni80 wire in general. Our goal for our blogs and help guides is to answer as many questions as possible to help to explain the possibilities of mesh to our customers.
We also offer similar products through our highly popular eBay store, check us out there too.
Contact our team today if you have any questions at all. We are always really keen to help in any way that we can.