With the continuous evolution of technology, new terminologies are constantly emerging. The terms flat wire and ribbon wire may seem interchangeable to the casual observer. Even so, closer examination reveals distinct differences, applications, and advantages between them. To understand what separates flat wire from ribbon wire, let’s take a look at how they differ today.
What is Flat Wire and Ribbon Wire?
Flat Wire: As its name suggests, flat wire has a flattened, wide, and thin cross-sectional shape. This characteristic shape is achieved by rolling round wire between flat surfaces, which compresses and spreads out the material.
Ribbon Wire: Ribbon wire refers to multiple conductors (or wires) running side by side, encapsulated in a flat, flexible insulating material. Each conductor within a ribbon wire is usually round in cross-section.
Key Differences Between Flat Wire and Ribbon Wire
Physical Structure: The primary distinction is their structural make-up. Flat wire is a single conductor that has been flattened, whereas ribbon wire consists of multiple conductors lying parallel to each other, encased within an insulator.
Applications: Flat wires are commonly used in applications that demand high flexibility, such as in certain types of speakers, transformers, and motor windings. Ribbon wires, on the other hand, are predominantly used in applications requiring multiple connections in a compact space like in computer peripherals, data transmissions, and IDC (Insulation Displacement Connector) systems.
Flexibility and Bending Radius: Flat wires, due to their singular conductor design, often provide greater flexibility in specific dimensions. Ribbon wires, having multiple conductors, may not be as flexible but offer a structured way to keep several connections organised.
Space and Efficiency: Flat wires can be tightly wound, allowing them to fit in narrow spaces. This makes them preferred for applications like winding coils where space conservation is essential. Ribbon wires, however, ensure multiple connections remain in a defined order, optimising the organisation in devices.
Benefits of Flat Wire
High Surface Area: The expanded surface area of flat wire facilitates improved heat dissipation and can carry more current than a round wire of the same cross-sectional area.
Space Efficiency: The unique shape allows for tight coil windings, making it an ideal choice for applications like motors and transformers where space is a concern.
Flexibility: The flattened profile can bend easier in one dimension, making it suitable for applications requiring flexibility.
Benefits of Ribbon Wire
Organised Connections: With multiple conductors running parallel, ribbon wires help maintain an organised connection system, crucial in complex devices and electronics.
Easy Identification: Ribbon wires often come with color-coded insulation for each conductor, making identification and connection simpler.
Compactness: By housing several wires in a single, flat profile, ribbon wire helps in conserving space and reducing clutter.
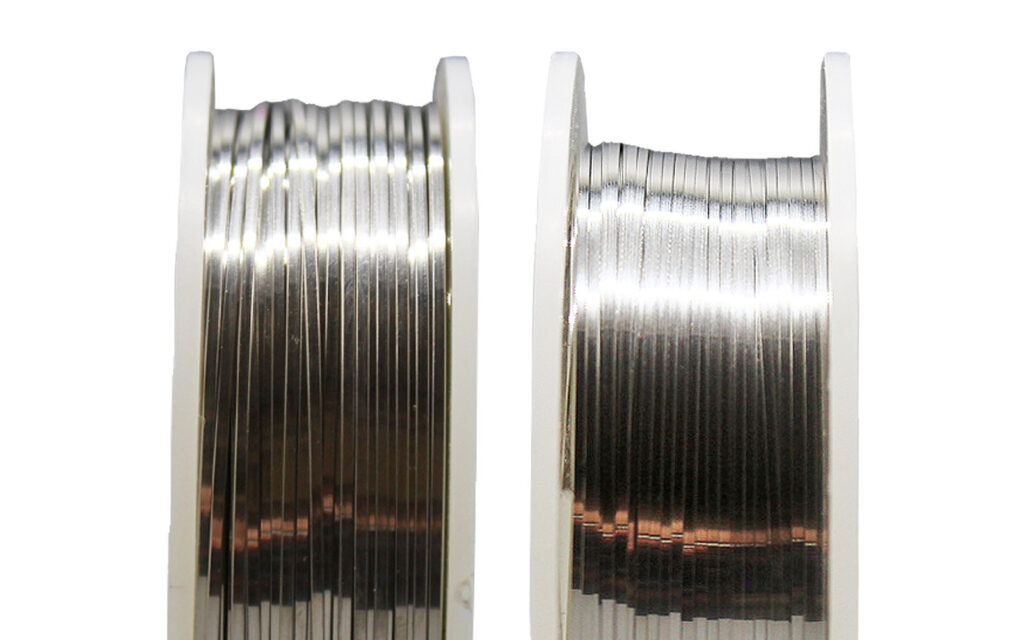
Uses of Flat Wire:
Transformers and Inductors: Flat wire coils in transformers and inductors can increase winding space efficiency and provide better heat dissipation due to their high surface area.
Speaker Voice Coils: Flat wire’s ability to be wound tightly makes it ideal for speaker voice coils, where it can help produce clearer sound and increase the power density of the coil.
Orthodontic Devices: In the medical field, flat wires are used in orthodontic braces and retainers.
Automotive: Flat wire springs are utilised in various automotive applications due to their space efficiency and load-bearing capabilities.
Electrical Contacts: Flat wires can be used to make electrical contacts, such as in switches or relays, given their shape and large surface area.
Solar Panels: Flat wires are sometimes used in photovoltaic ribbon cables, which interconnect solar cells.
Jewelry and Decorations: Due to their shape and flexibility, flat wires are popular in jewelry-making and various craft projects.
Uses of Ribbon Wire:
Electronics and Computer Peripherals: Ribbon cables are used to connect internal components of computers, like hard drives, CD drives, and certain types of motherboards.
Data Transmission: Due to the parallel architecture of ribbon wires, they’re used in data transmission applications where multiple signals need to be sent simultaneously.
IDC Systems (Insulation Displacement Connector Systems): Ribbon cables are commonly connected using IDC connectors, which allow multiple connections to be made in a single action without stripping the insulation from individual wires.
Telecommunications: Ribbon wire is often used in telecommunication setups to connect multiple channels.
Consumer Electronics: Devices like printers, scanners, and testing equipment often use ribbon cables for internal connections.
Laboratory Instrumentation: Due to their ability to handle multiple connections neatly, ribbon wires are used in various lab instruments.
Flat Panel Displays: Ribbon cables are utilised in the internal connections of flat-panel displays like LCDs.
Choosing Between Flat Wire and Ribbon Wire
The decision to opt for flat wire or ribbon wire largely depends on the application in question:
For High Flexibility: If your primary concern is flexibility, especially in one dimension, flat wire would be a better choice.
For Multiple Connections: For applications requiring multiple parallel connections in an organised and compact manner, ribbon wire stands out.
Space Considerations: If you are looking to wind coils tightly and save on space, flat wire’s unique shape offers an advantage. But, if you’re thinking of conserving space while maintaining multiple connections, ribbon wire is the way to go.
The debate between flat wires and ribbon wires is not necessarily about which is better. Rather than highlighting their similarities, it emphasises what makes them unique. You can choose the most appropriate wire type for your specific needs by understanding its fundamental differences, applications, and benefits.
Understanding the nuances of the materials and tools available to you can greatly enhance your projects’ efficiency and functionality. Having knowledge of flat wire’s flexibility or ribbon wire’s organised structure ensures you make the best decision for your application.
We offer also a massive range of stainless steel wire and nichrome wire through our store. Choose the wire that you want to work with and we’ll get spooling.
If you’re interesting in learning more about wire, check out our other blog on Everything You Need to Know About Wires.
We are also proud to supply this product on our highly popular eBay store, check us out there too.
Thank you for checking out our site.

Nichrome Wire Safety: Top Tips for Working Safely

Best Wire for Electronics Projects

Is Ni80 Wire Suitable for DIY Heating Elements

Wire Grades Explained

How Wire Diameter Affects Strength and Flexibility

How to Cut and Shape Wire for Custom Applications

Can Wire Be Used in 3D Printing?

How Wire Composition Affects Conductivity